When clients come to see me and they want to start progressing their strength and build on what they learn in class I always suggest doing some work at home. Fairly obviously most people don’t have time or the money or the energy to come to a class daily and I don’t think that would be great for you anyway. What I do think helps is chipping away at strength foundations every day if that’s possible for you. I definitely don’t mean for an hour every day, and I definitely don’t mean an intense session more than 3 times a week, maybe even less.
What to consider when starting/committing to a movement practice:
1) Know Yourself! Personally I really struggle with high intensity exercise - maybe I used up all my intense sessions when I was rowing and doing CrossFit and I’ve got none left now? If you respond well and feel great after intense sessions, that’s great, monitor the best response you get from your body with how many per week suits you - 4 may be too many and leave you depleted, 1 may be too few as it may make you feel a bit sluggish in each session. Again this is my personal experience: I do respond well to strength workouts, I am slightly hypermobile so I need more strength than anything else (hence Pilates and not yoga for me). Some women come in and talk to me saying they do circuits or running or something similar and feel a bit wobbly and are in pain afterwards, or drained and exhausted but don’t recognise this. At the time I was doing it, Crossfit was not a good workout system for me, I would get constantly injured and feel sore and depleted for days after each session.
2) Does your routine serve you well? If you are recently post-natal or coming out of the pre-school years and now wanting to focus on yourself, monitor how your pelvic floor, abdominals and any shoulder and back pain responds to the new exercise/movement regime. If you are in pain or have issues with leaking or a pooch tummy, don’t accept this as your new normal or just how it will be because of having babies, your movement practice should serve to strengthen and benefit you, helping you to build foundations in the right way, not in a more depleting way causing any further issues. If you start leaking, feel more weak in your centre, have lasting shoulder, neck or back pain and aren’t able to move well in your daily life, take some time to think about your movement practice and whether there might be something there that isn’t working for you.
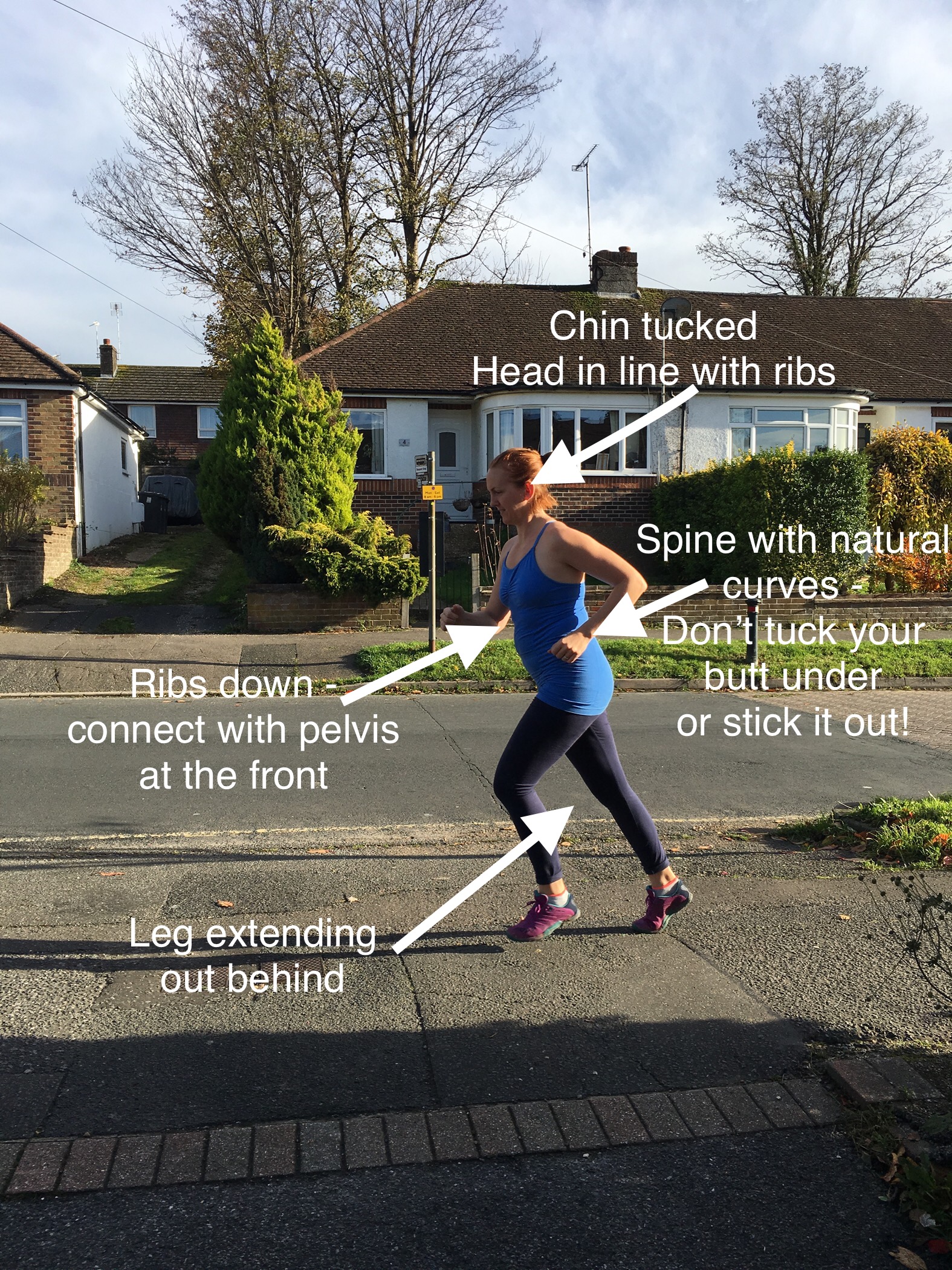
3) “Listen to the whispers so you don’t have to hear the shouts”!! After years of struggling to find the right way, I’ve built, over time, better foundations, which I continue to work on all the time: breathing, pelvic floor awareness, rib mobility, spine elongation, glute strength, and now I can build overall strength and dynamics on top of that. Take care not to go in hard straight away, getting over enthused by being unleashed into the world of movement after feeling like your body belongs to someone else for a few years. I totally understand the thinking, it feels so good to move, but this is also a moveable feast, your response to movement will change daily, weekly, monthly and so some exercise will suit you one day and feel all kinds of wrong the next. Of course our menstrual cycle affects that, as well as the physical demands we have from others day to day, as a woman ending her child bearing life phase and moving on to the next we also have influences from post-birthing and feeding hormones as well as the coming peri-menopause symptoms. You may have to become more aware of your needs and responses as you go on.
4) What to do and how often? My personal commitment and what works for me is to do a max 10 minute glute mini workout often in front of the TV in the evening or between working on admin stuff during the day and then 2-3 longer workouts like this one ☝🏼 each week. I’ll do my rehab stuff as often as possible too (there’s always something needing doing) and I run with my dog, as long as I’m not injured, twice a week - this is often a walk and not a run, always on trails and hilly or rough ground. This works for me as I know I can fit in at least 2 longer sessions each week on days that I work less, and I know that if I don’t do some extra glute work through the week, my hips and back get achy and tired, and I need the correct support from my core to be able to move, sit while working for long periods, and do my job. The running happens if I can because I might as well use the time I walk my dog to do a bit of extra sweating. I put no pressure on myself with this, running is not my natural thing, but I do love the enjoyment of moving faster than walking, sweating and pushing myself a bit.
When you are looking at this you may think, “oh I could never do something every day” or “I could never do 2 longer sessions, I just don’t have the time”, so this is where you look at what time you do have, what you’d really love to do, who you could ask to support you to be able to choose that option (see previous blog post) and maybe what you might have to give up to make that commitment. Often if we look at it, there are slack times in our day when we don’t need to spend half an hour scrolling Instagram ( yes, me too, it’s a sap!) or an hour watching TV in the evening - actually a useful time to consciously move. I’ve had good responses with women willing to do a short circuit while cooking dinner in the evening - the trick here is being prepared so you’re at least in comfortable clothes ready to move when you have the opportunity.
5) Values - in the end your choice of movement comes down to your values for yourself. Where do you want to get to? What does your future look like and your ideal week of movement entail if time and money were no object? Moving in a nourishing way is a show of self-love, loving yourself enough to honour the adventure that you and your body have been in through your life, showing yourself how brilliant you are for housing, nourishing and nurturing another human and giving yourself the space to rebuild with all that you have experienced inside you now.
Have you found your way with your workout/exercise/sport/movement routine? Are you struggling to work things out? Do you want help and to find a way?
As a post-natal corrective exercise specialist I see women 1-1 in both my studio in Sussex and online from anywhere in the world, get in touch to chat over your needs and how I can help you.